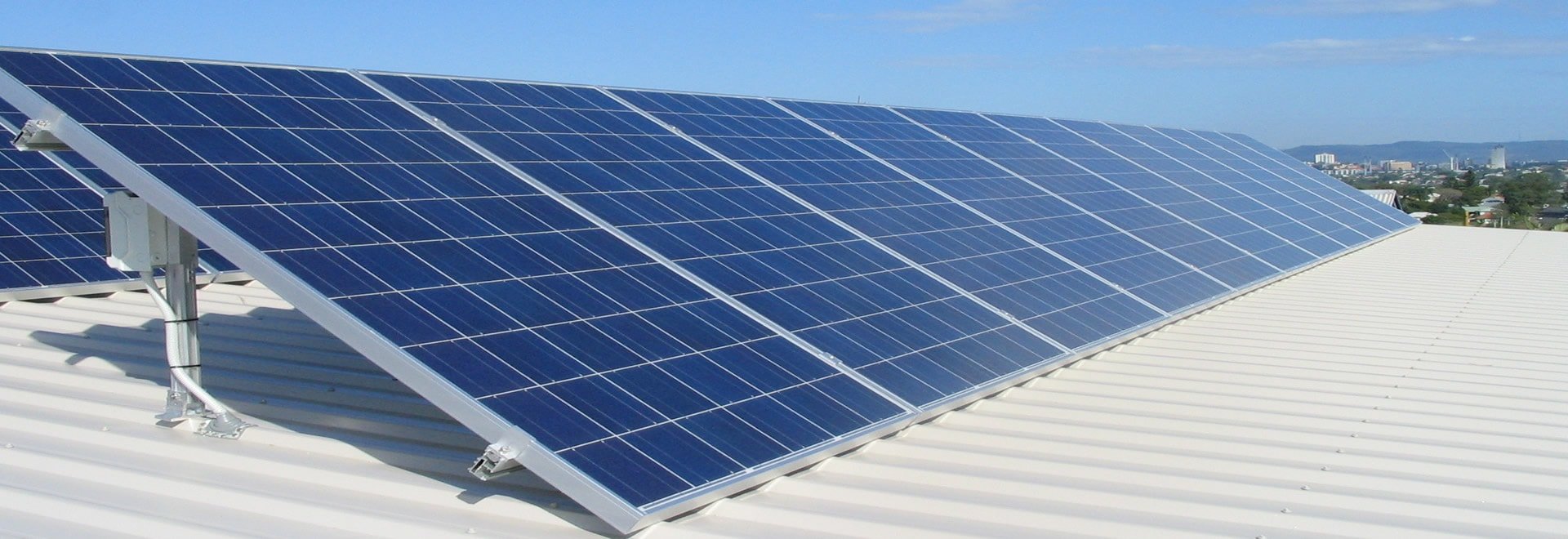
A photovoltaic cell is a specialized semiconductor diode that converts visible light into direct current. Photovoltaic cells are becoming increasingly important as alternative sources of utility power. Large sets of PV cells can be connected together to form solar modules, arrays, or panels. The use of PV cells and batteries for the generation of usable electrical energy is known as photovoltaic. Once a photovoltaic system has been installed, it can provide energy at essentially no cost for years, and with minimal maintenance.
There are two basic types of semiconductor material, called positive and negative. In a PV cell, flat pieces of these materials are placed together, and the physical boundary between them is called the P-N junction. The device is constructed in such a way that the junction can be exposed to visible light. When such radiation strikes the P-N junction, a voltage difference is produced between the P type and N type materials. Electrodes connected to the semiconductor layers allow current to be drawn from the device.